Accommodation: the process by which the eye changes focus from one distance to another.
Adaptation: the process by which the visual system becomes accustomed to more or less light or of a different color than it was exposed to during an immediately preceding period. It results in a change in the sensitivity of the eye to light.
Arrangement: the repeating pattern of luminaires on a roadway. Usually described as opposite, staggered, one-side, center-suspended, or median mounted.
Ballast: a device used with an electric-discharge lamp to obtain the necessary circuit conditions (voltage, current and waveform) for starting and operating.
Beacon lighting: a single luminaire that will identify the presence of an intersection or an interchange or potential conflict with other traffic and physical features and will serve as a warning or marker.
Bifurcation area: the triangular shaped area between two diverging lanes, beyond the point of physical separation of one lane from the other. This area is immediately beyond the decision point where a driver must commit to one lane or the other, and lies in the direct line of travel of an overrunning vehicle.
bidirectional reflectance-distribution function (BRDF): the ratio of the differential luminance of a ray reflected in a given direction to the differential luminous flux density incident from a given direction of incidence, which produces it.
Bikeway: any road, street, path, or way that in some manner is specifically designated as being open to bicycle travel, regardless of whether such facilities are designated for the exclusive use of bicycles or are to be shared with other transportation modes.
Brightness: see luminance and subjective brightness.
Candela, cd: the SI unit of luminous intensity. One candela is one lumen per steradian. Formerly candle. (See Figure 50.)
Candela per square meter, Cd/m2: the SI unit of luminance equal to the uniform luminance of a perfectly diffusing surface emitting or reflecting light at the rate of one lumen per square meter or the average luminance of any surface emitting or reflecting light at that rate.
Candlepower, cp: luminous intensity expressed in candelas. (It is no indication of the total lumen output)
Central (foveal) vision: the seeing of objects in the central or foveal part of the visual field, approximately two degrees in diameter. It permits seeing much finer detail than does peripheral vision.
Contrast sensitivity: the ability to detect the presence of luminance differences. Quantitatively, it is equal to the reciprocal of the contrast threshold.
contrast see luminance contrast.
Contrast threshold: the minimal perceptible contrast for a given state of adaptation of the eye. It also is defined as the luminance contrast detectable during some specific fraction of the times it is presented to an observer, usually 50 percent.
Conflict: A conflict occurs whenever the paths followed by vehicles diverge, merge or cross
Conflict Area:I s an area of a roadway where the motorist's special attention is required in order to interpret the functional features (e.g. bullnose) and / or activities (e.g. pedestrians, turning vehicles, railroad grade crossing) of the roadway, in order to make a decision on their driving routine. It is that area which encompasses all of the conflict points.
Conflict Points: Points at which conflicts can occur.
Continuous Lighting: A fixed overhead lighting system designed to provide a specific level of illuminance, luminance and uniformity of light on the roadway throughout a highway complex.
Crosswalk: see pedestrian crosswalk.
Diffuse reflectance: the ratio of the flux leaving a surface or medium by diffuse reflection to the incident flux.
Directional reflectance: the reflectance in a given direction from an incident ray reaching the surface or medium from a given direction. See bidirectional reflectance-distribution function.
Disability glare: glare resulting in reduced visual performance and visibility. It often is accompanied by discomfort. See veiling luminance.
Discomfort glare: glare producing discomfort. It does not necessarily interfere with visual performance or visibility.
Entrance Ramp Conflict Area: That area of an entrance ramp from the bullnose (covering both the ramp lane(s) and the right through lane) to the end of the ramp taper.
Exit Ramp Conflict Area: That area of an exit ramp and the right through lane from the beginning point of the bifurcation area (neutral area) to the end of the gore area and extended 15 to 40 meters – dependant on the design speed – for both the ramp lane(s) and the right through lane.
Footcandle, fc: the unit of illuminance when the foot is taken as the unit of length. It is the illuminance on a surface one square foot in area on which there is a uniformly distributed flux of one lumen, or the illuminanceproduced on a surface all points of which are at a distance of one foot from a directionally uniform point source of one candela.
Glare: the sensation produced by luminance within the visual field that is sufficiently greater than the luminance to which the eyes are adapted to cause annoyance, discomfort, or loss in visual performance and visibility. See disability glare, discomfort glare.
Intersection: the general area where two or more roadways (highways) join or cross, including the roadway and roadside facilities for trafficmovement within it.
Intersection Conflict Area: That area of an intersection that is extended to cover the conflict area
Lambertian surface: a surface that emits or reflects light in accordance with Lambert's cosine law. A Lambertian surface has the same luminance regardless of viewing angle.
Lamp: a generic term for an artificial source of light.
Lamp life: the average life of a lamp defined as the total operating hours at which 50 percent of any group of lamps is still operating.
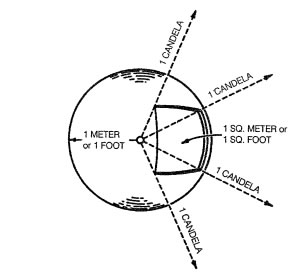
Figure 2 – Relationship between candelas, lumens, lux, and footcandles:
A uniform point source (luminous intensity or candlepower = one candela) is shown at the center of a sphere of unit radius whose surface has a reflectance of zero. The illuminance at any point on the sphere is one lux (one lumen per square meter) when the radius is one meter, or one footcandle (one lumen per square foot) when the radius is one foot. The solid angle subtended by the area A,B,C,D is one steradian. The flux density is therefore one lumen per steradian, which corresponds to a luminous intensity of one candela as originally assumed. The sphere has a total area of 4 (or 12.57) square units (square meters or square feet), and there is a luminous flux of one lumen falling on each unit area. Thus the source provides a total of 12.57 lumens.
High mast lighting: illumination of a large area by means of a group of luminaires which are designed to be mounted in fixed orientation at the top of a high support or pole (generally 20 meters or higher).
Illuminance, E: the density of the luminous flux incident on a surface; it is the quotient of the luminous flux by the area of the surface when the latter is uniformly illuminated.
Illuminance (lux or footcandle) meter: an instrument for measuring illuminance on a plane. Instruments which accurately respond to more than one spectral distribution (color) are color corrected. Instruments which accurately respond to more than one spatial distribution of incident flux are cosine corrected. The instrument is comprised of some form of photo-detector with or without a filter, driving a digital or analog readout through appropriate circuitry.
Intensity: a shortening of the terms luminous intensity and radiant intensity.
Lamp lumen depreciation factor, LLD: the multiplier to be used in calculations to relate the initial rated output of light sources to the anticipated minimum output based on the relamping program to be used.
Lamp post: a support or pole provided with the necessary internal attachments for wiring and the external attachments for the bracket and/or luminaire.
Light loss factor, LLF: a factor used in a lighting calculation after a given period of time and under given conditions. It takes into account temperature and voltage variations, dirt accumulation on luminaire surfaces, lamp lumen depreciation, maintenance procedures, equipment and ballast variations. Formerly called maintenance factor.
Line of sight: the line connecting the point of observation and the point of fixation.
Lumen, lm: the SI unit of luminous flux. Radiometrically, it is determined from the radiant power. Photometrically, it is the luminous flux emitted within a unit solid angle (one steradian) by a point source having a uniform luminous intensity of one candela.
Luminaire: a complete lighting unit consisting of a lamp or lamps together with the parts designed to distribute the light, to position and protect the lamps and to connect the lamps to the power supply. Sometimes includes ballasts and photocells.
Luminaire cycle: the distance between two luminaires along one side of the roadway. Note: this may not be the same as luminaire spacing along the centerline considering both sides of the road. (See spacing.)
Luminaire dirt depreciation factor, LDD: the multiplier to be used in lighting calculations to reduce the initial light level provided by clean, new luminaires to the light level that they willprovide due to dirt collection on the luminaires at the time at which it is anticipated that cleaning procedures will be instituted.
Luminance, L (cd/m2): the quotient of the luminous flux at an element of the surface surrounding the point, and propagated in directions defined by an elementary cone containing the given direction, by the product of the solid angle of the cone and area of the orthogonal projection of the element of the surface on a plane perpendicular to the given direction.The luminous flux may be leaving, passing through, and/or arriving at the surface. Note: In common usage the term "brightness" usually refers to the strength of sensation which results from viewing surfaces or spaces from which light comes to the eye. This sensation is determined in part by the definitely measurable luminance defined above and in part by conditions of observation such as the state of adaptation of the eye.
Luminance contrast: the relationship between the luminances of an object and its immediate background.
Luminance meter: an instrument for measuring the luminance of an object or surface. Instruments which accurately respond to more than one spectral distribution (color) are color corrected. The instrument is comprised of some form of a lens system and aperture creating an image on a photodetector, driving a digital or analog readout through appropriate circuitry.
Luminous efficacy of a source of light: the quotient of the total luminous flux emitted by the total lamp power input. It is expressed in lumens per watt.
Luminous flux density at a surface: the luminous flux per unit area at a point on a surface. Note: this need not be a physical surface; it may equally well be a mathematical plane.
Luminous intensity, I (cd): the luminous flux per unit solid angle in a specific direction.Hence, it is the luminous flux on a small surface normal to that direction, divided by the solid angle (in steradians) that the surface subtends at the source.
Lux, lx: the SI unit of illuminance. It is the illuminance on a surface one square meter in area on which there is a uniformly distributed flux of one lumen, or the illuminance produced at a surface all points of which are at a distance of one meter from a uniform point source of one candela.
Mean lamp lumens: the mean lumen output of a lamp is calculated by determining the area beneath the lumen maintenance characteristic curve of that source over a given period of time and dividing that area by the time period in hours.
Mounting height, MH: the vertical distance between the roadway surface and the center of the apparent light source of the luminaire.
Overhang, OH: the horizontal distance between a vertical line passing through the luminaire light center and the curb or edge of the travelled roadway.
Partial Lighting: Partial Lighting refers to lighting installed at the decision areas of isolated interchanges and intersections whereby it provides visibility of potential conflicts with other traffic and physical features.
Pedestrian crosswalk: an area designated by markings for pedestrians to cross the roadway.
Pedestrian way: a sidewalk or pedestrian walkway, usually paved, intended for pedestrian usage.
Point of fixation: a point or object in the visual field at which the eyes look and upon which they are focused.
R-table: a table for a particular pavement type which provides reduced luminance coefficients in terms of the variable angles, beta and tan gamma.
Reaction time: the interval between the beginning of a stimulus and the beginning of the response of an observer.
Setback: the lateral offset of the pole center from the face of the curb or edge of the travelled way.
Spacing: the distance between successive luminaires measured along the center line of the street. See luminaire cycle.
Spacing-to-mounting height ratio, S/MH: the ratio of the distance between luminaire centers, along the center line of the street, to the mounting height above the roadway.
Subjective brightness: the subjective attribute of any light sensation given rise to the perception of luminous intensity, including the whole scale of qualities of being bright, lightness, brilliant, dim, or dark.
Traffic conflict area: area on a road system where a strong potential exists for collisions between vehicles or between vehicles and pedestrians.
Veiling luminance: a luminance superimposed on the retinal image which reduces its contrast. It is this veiling effect produced by bright sources or areas in the visual field that results in decreased visual performance and visibility.
Visibility: the quality or state of being perceivable by the eye. In many outdoor applications, visibility is sometimes defined in terms of the distance at which an object can be just perceived by the eye. In indoor and out- door applications it usually is defined in terms of the contrast or size of a standard test object, observed under standardized view-conditions, having the same threshold as the given object.
Visibility index, VI: a measure closely related to visibility level sometimes used in connection with road lighting applications.
Visibility level, VL: a contrast multiplier to be applied to the visibility reference function or provide the luminance contrast required at different levels of task background luminance to achieve visibility for specified conditions relating to the task and observer.
Visual angle: the angle subtended by an object or detail at the point of observation. It usually is measured in minutes of arc.
Walkway: a sidewalk or pedestrian way.
